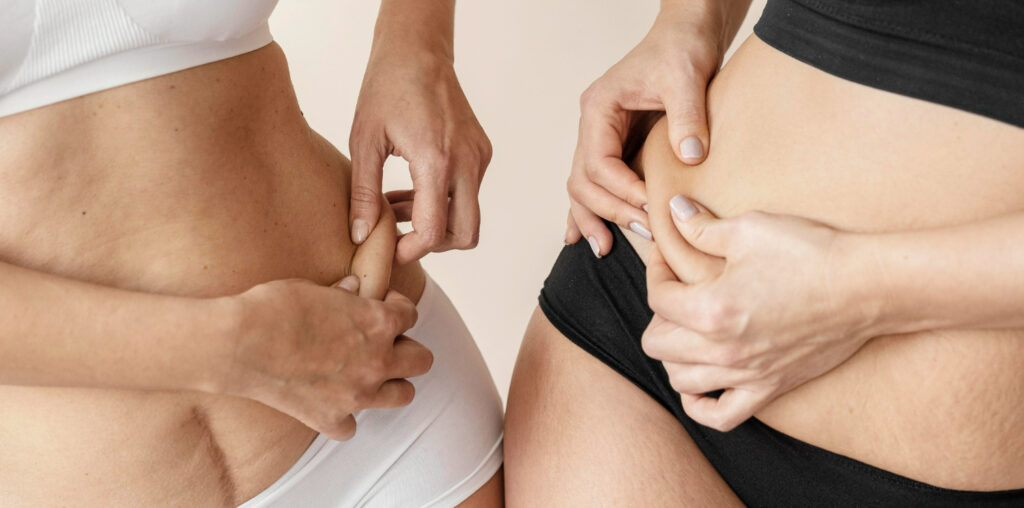
In recent years, the search for effective weight loss solutions has led to the emergence of innovative medications, with semaglutide standing out as a promising option. Originally developed for managing type 2 diabetes, semaglutide has garnered attention for its potential to aid in weight loss. This blog delves into the science behind semaglutide, its mechanisms, effectiveness, potential side effects, and considerations for those considering it as a weight loss option.
Understanding Semaglutide
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a synthetic glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue, which means it mimics a hormone that plays a critical role in glucose metabolism. It is administered via injection and has been approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes under the brand names Ozempic and Rybelsus, as well as for weight management under the brand name Wegovy.
How Does Semaglutide Work?
Semaglutide works by activating GLP-1 receptors in the brain and the gastrointestinal tract. This action leads to several physiological responses that contribute to weight loss:
- Appetite Regulation: Semaglutide promotes a feeling of fullness, helping to reduce overall calorie intake.
- Delayed Gastric Emptying: It slows the rate at which food leaves the stomach, contributing to increased satiety.
- Glucose Control: By improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood sugar levels, semaglutide helps to mitigate cravings and stabilize energy levels.
The Effectiveness of Semaglutide for Weight Loss
Clinical Trials and Research
The effectiveness of semaglutide for weight loss has been demonstrated in several clinical trials. One of the most notable studies, the STEP (Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity) trials, involved over 4,500 participants with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher (or 27 or higher with weight-related comorbidities). The results revealed:
- Significant Weight Loss: Participants lost an average of 15-20% of their body weight over 68 weeks when combined with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
- Sustained Results: Weight loss was not only significant but also sustainable over time, with participants maintaining a substantial portion of their weight loss even after the trial ended.
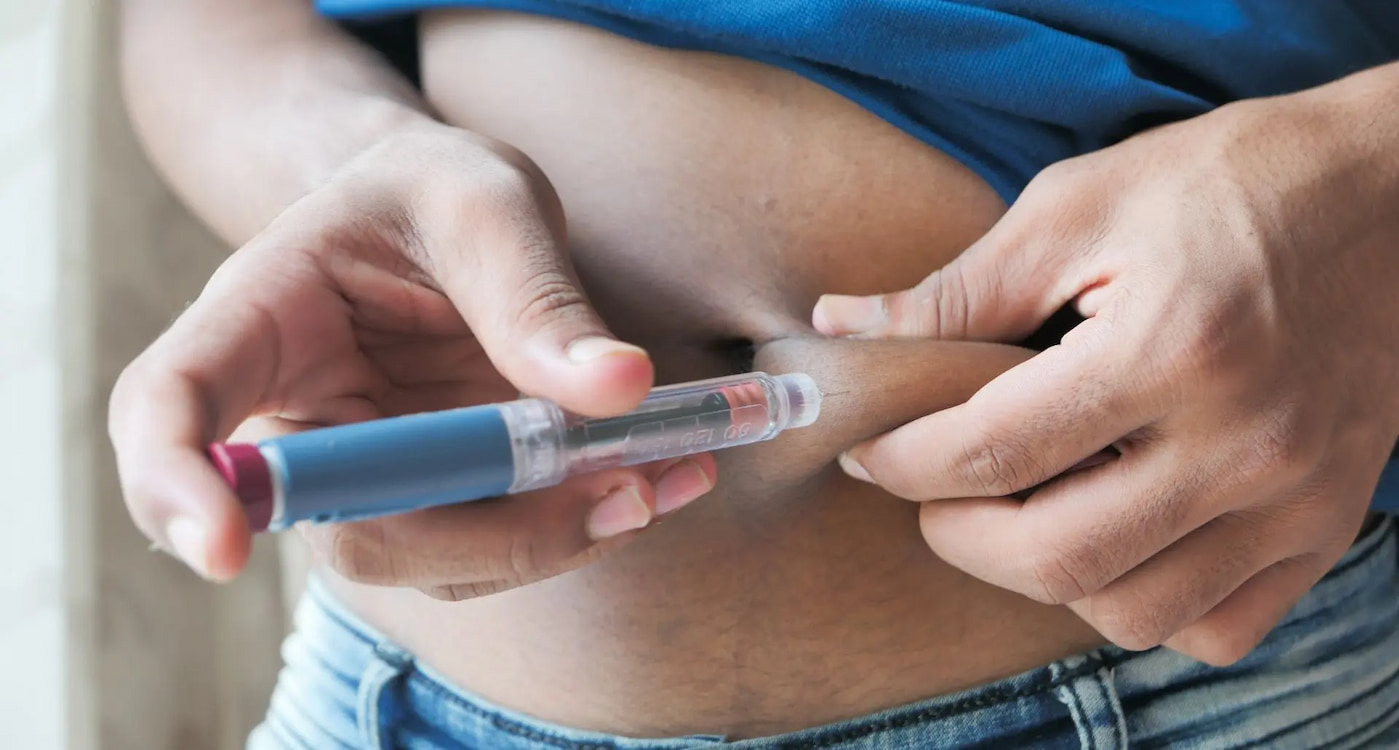
Comparison with Other Weight Loss Medications
When compared to traditional weight loss medications, semaglutide has shown superior results. While many weight loss drugs lead to modest weight loss (5-10% of body weight), semaglutide’s clinical trials suggest that individuals can expect a much greater reduction in weight. This makes semaglutide a viable option for those struggling with obesity and looking for effective treatment.
Potential Side Effects of Semaglutide
While semaglutide presents a promising option for weight loss, it is essential to be aware of potential side effects. Common side effects include:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain are frequently reported. These symptoms often decrease over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Hypoglycemia: Particularly in patients with diabetes, semaglutide can lead to low blood sugar levels, especially when taken in conjunction with other diabetes medications.
- Injection Site Reactions: Some individuals may experience redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
In rare cases, semaglutide has been associated with more severe side effects, including:
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas can occur, leading to severe abdominal pain.
- Thyroid Tumors: Animal studies have suggested a potential risk of thyroid tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). Though this risk has not been conclusively shown in humans, it is a concern that warrants discussion with a healthcare provider.
- Kidney Problems: Some patients have reported kidney injury, particularly those experiencing severe gastrointestinal symptoms.
Who Should Consider Semaglutide for Weight Loss?
Eligibility Criteria
Semaglutide is primarily indicated for adults with obesity (BMI ≥30) or overweight (BMI ≥27) with weight-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or dyslipidemia. Before starting semaglutide, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider who can assess individual health status, weight loss goals, and potential contraindications.
Not Suitable For Everyone
Semaglutide is not recommended for individuals with:
- A personal or family history of MTC or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
- A known hypersensitivity to semaglutide or any of its components.
- Severe gastrointestinal disease or diabetic gastroparesis.
How to Use Semaglutide
Administration Guidelines
Semaglutide is typically administered as a subcutaneous injection once a week. Here are some essential guidelines for using semaglutide effectively:
- Start Low and Go Slow: To minimize gastrointestinal side effects, the treatment usually starts at a lower dose, gradually increasing over several weeks until the target dose is reached.
- Consistency is Key: It is essential to administer the injection on the same day each week to maintain stable levels in the bloodstream.
- Diet and Exercise: For optimal results, semaglutide should be combined with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity. A healthcare provider or a nutritionist can help create a personalized plan.
Monitoring Progress
Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are vital to monitor weight loss progress, assess side effects, and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Keeping track of dietary intake and physical activity can further enhance the effectiveness of semaglutide.
Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Weight Loss
Nutrition and Diet
While semaglutide can help control appetite and reduce cravings, adopting a balanced diet is crucial for sustainable weight loss. Here are some dietary tips to consider:
- Focus on Whole Foods: Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals.
- Monitor Portion Sizes: Be mindful of portion sizes, as even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water can help control hunger and support overall health.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for weight loss and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, along with strength training exercises on two or more days. Activities can include walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or group fitness classes.
Behavioral Changes
Adopting healthy behaviors can also support weight loss efforts. Consider the following strategies:
- Set Realistic Goals: Establish achievable weight loss goals to stay motivated and focused.
- Practice Mindful Eating: Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues to prevent overeating.
- Seek Support: Joining a weight loss group or seeking support from friends and family can provide encouragement and accountability.
Conclusion
Semaglutide has emerged as a groundbreaking treatment option for weight loss, offering hope for those struggling with obesity and related health conditions. With its proven effectiveness in clinical trials, semaglutide can help individuals achieve significant weight loss and improve overall health.
However, it is essential to remember that semaglutide is not a standalone solution. Combining this medication with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and healthy lifestyle changes is crucial for long-term success. As with any medical treatment, consulting a healthcare provider is vital to determine if semaglutide is the right choice for you and to develop a comprehensive weight management plan.
As the obesity epidemic continues to rise, innovative solutions like semaglutide represent a promising avenue for those seeking effective weight loss strategies. With ongoing research and development, the future of weight management may hold even more exciting possibilities.