Introduction
Dopamine agonists play a crucial role in gynecology and endocrinology, particularly in managing hyperprolactinemia, menstrual disorders, infertility, and prolactinomas. Among these, Cabergoline (brand name Dostinex) stands out as a highly effective treatment. Available in doses of 0.25 mg and 0.5 mg, Cabergoline effectively lowers prolactin levels, restores normal menstrual cycles, improves fertility, and shrinks prolactin-secreting pituitary tumors.
This article explores the mechanisms, clinical applications, dosages, and benefits of Cabergoline in treating hyperprolactinemia-related conditions.
Understanding Hyperprolactinemia and Its Impact
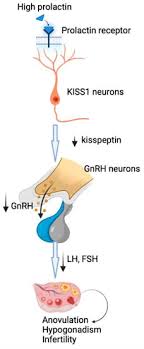
Hyperprolactinemia—a condition marked by elevated prolactin levels—can disrupt reproductive and endocrine functions. Prolactin, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, primarily stimulates milk production postpartum. However, excessive prolactin secretion leads to:
- Menstrual irregularities (amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea)
- Infertility (anovulation, luteal phase defects)
- Galactorrhea (inappropriate milk production)
- Hypogonadism (low estrogen or testosterone)
- Prolactinomas (benign pituitary tumors)
Dopamine agonists like Cabergoline suppress prolactin secretion by activating dopamine D2 receptors in the pituitary gland.
Cabergoline: Mechanism of Action
Cabergoline is a long-acting dopamine receptor agonist with high selectivity for D2 receptors. Its key pharmacological properties include:
- Strong prolactin-lowering effects – Binds to pituitary lactotrophs, inhibiting prolactin synthesis and release.
- Extended half-life (63–69 hours) – Allows for once or twice-weekly dosing, improving patient compliance.
- Tumor shrinkage in prolactinomas reduces tumor size by decreasing prolactin-secreting cell activity.
Compared to older agents like Bromocriptine, Cabergoline offers better tolerability, fewer side effects, and superior efficacy.
Clinical Uses of Cabergoline in Gynecology and Endocrinology
1. Treating Hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia causes anovulation, infertility, and menstrual disorders. Cabergoline normalizes prolactin levels, restoring:
- Regular menstruation in women with amenorrhea/oligomenorrhea
- Ovulatory cycles, improving fertility
- Reduction in galactorrhea
Dosage:
- Initial dose: Cabergoline 0.25 mg twice weekly (can be increased to Cabergoline 0.5 mg twice weekly if needed)
- Maintenance dose: Adjusted based on prolactin levels (usually 0.25–1 mg per week)
2. Managing Prolactinomas
Prolactinomas (prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas) are the most common functional pituitary tumors. Symptoms include:
- Headaches, vision problems (if the tumor compresses the optic chiasm)
- Hypogonadism (due to suppressed GnRH)
Cabergoline effectively:
- Lowers prolactin levels
- Shrinks tumor size (even in macroadenomas >10 mm)
- Restores gonadal function
Dosage for Prolactinomas:
- Starting dose: 0.25 mg twice weekly
- Gradually increase (up to 1–2 mg weekly) based on response
- Long-term therapy is often required to prevent recurrence
3. Improving Fertility in Women with Hyperprolactinemia
Elevated prolactin inhibits GnRH secretion, leading to anovulation and infertility. Cabergoline:
- Restores ovulation
- Enhances pregnancy rates in women undergoing fertility treatments
- Safe during early pregnancy (discontinued once pregnancy is confirmed)
Note: While Cabergoline is not teratogenic, most clinicians stop it post-conception unless the tumor is large or symptomatic.
4. Off-Label Uses
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Some studies suggest Cabergoline improves insulin sensitivity and hyperandrogenism in PCOS with mild hyperprolactinemia.
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS): May alleviate symptoms in women with cyclical hyperprolactinemia.
Cabergoline Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosing Guidelines
| Condition | Starting Dose | Maintenance Dose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hyperprolactinemia | 0.25 mg | 0.25–1 mg | Twice weekly |
| Prolactinomas | 0.25 mg | 0.5–2 mg | Twice weekly |
| Fertility Treatment | 0.25 mg | Adjusted based on prolactin | Twice weekly |
Key Administration Tips
✔ Take with food to minimize nausea.
✔ Start low, go slow to reduce side effects.
✔ Monitor prolactin levels every 4–6 weeks.
✔ MRI follow-up for prolactinomas (assess tumor shrinkage).
Side Effects and Safety Considerations
Cabergoline is generally well-tolerated, but potential side effects include:
- Common: Nausea, dizziness, headache, fatigue
- Less common: Orthostatic hypotension, constipation, nasal congestion
- Rare but serious:
- Valvular heart disease (with very high doses, as seen in Parkinson’s treatment)
- Psychiatric effects (impulse control disorders, hallucinations)
Contraindications:
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- History of cardiac valve fibrosis
- Hypersensitivity to ergot derivatives
Cabergoline vs. Bromocriptine: Which is Better?
| Feature | Cabergoline | Bromocriptine |
|---|---|---|
| Dosing Frequency | 1–2 times weekly | 2–3 times daily |
| Side Effects | Lower incidence | More nausea, dizziness |
| Efficacy | Higher success rate | Moderate efficacy |
| Tumor Shrinkage | More pronounced | Less consistent |
| Cost | More expensive | Cheaper |
Conclusion: Cabergoline is preferred due to better tolerability, convenience, and efficacy.
Conclusion
Cabergoline (Dostinex 0.25 mg and 0.5 mg) is a first-line dopamine agonist for hyperprolactinemia, prolactinomas, and related infertility. Its long half-life, strong prolactin-lowering effects, and tumor-shrinking capabilities make it superior to older therapies.
For women with menstrual disorders, infertility, or prolactinomas, Cabergoline offers a safe, effective, and convenient treatment option. Regular monitoring ensures optimal outcomes while minimizing risks.
By understanding its mechanisms, dosages, and clinical applications, healthcare providers can effectively manage hyperprolactinemia and improve patients’ reproductive health.