In the fast-evolving world of electronics, managing heat effectively has become a critical challenge. As devices grow more powerful, the need for advanced thermal management solutions has never been more urgent. From computers and gaming systems to telecommunications equipment and medical devices, every electronic component generates heat during operation. If left unmanaged, this heat can lead to performance throttling, component failure, or even permanent damage. To address this challenge, innovations in thermal management technology, such as the tubed cold plate, are becoming essential for maintaining optimal performance and reliability in electronic systems.
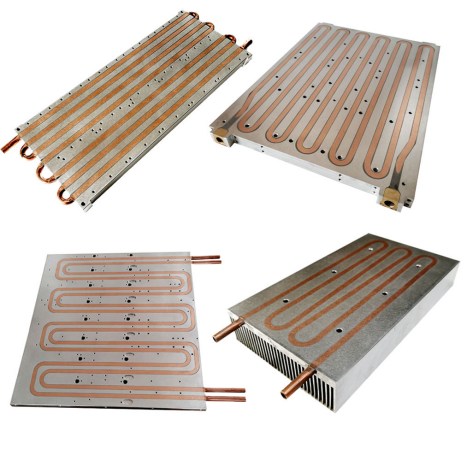
A tubed cold plate is a highly effective solution for transferring and dissipating heat from sensitive electronic components. By using a series of tubes embedded in a conductive plate, these systems are designed to rapidly absorb and redirect heat away from heat-sensitive components to ensure efficient cooling. They are becoming indispensable in industries that rely on high-performance electronics, such as computing, telecommunications, automotive, and medical technology.

What Are Tubed Cold Plates?
To fully appreciate how tubed cold plates revolutionize thermal management, it is important to first understand what they are and how they function. A tubed cold plate is a passive thermal management device that uses a series of small tubes embedded in a flat, conductive plate to manage heat. These tubes are filled with a coolant that circulates through the plate, carrying away heat from the components they are attached to.
In a typical tubed cold plate design, the plate itself is made of a high thermal conductivity material, such as copper or aluminum, which allows for efficient heat transfer. The tubes within the plate are typically arranged in a pattern that maximizes the surface area available for heat exchange, allowing the system to absorb more heat from the component. As the coolant inside the tubes absorbs the heat, it moves through the system, where it is ultimately dissipated by a radiator or other cooling mechanisms.
The advantage of this design lies in its ability to rapidly and efficiently distribute heat across a larger surface area, allowing for more effective cooling compared to traditional passive heat sinks.
Why Heat Management Is Crucial in Electronics
In any electronic system, managing heat is crucial for a variety of reasons.
- First and foremost, excessive heat can reduce the lifespan of components. Overheating can cause materials to degrade faster, leading to reduced performance or failure of parts over time. This is particularly problematic in systems that need to operate continuously or under heavy loads, such as servers, high-performance computing systems, or automotive electronics.
- Second, as components become smaller and more powerful, the density of heat generation increases. This is especially true in the case of processors, graphics cards, and power supplies, which generate large amounts of heat relative to their size. Without an efficient cooling system, these devices would quickly overheat, leading to performance throttling (where the system intentionally slows down to avoid overheating) or even complete failure.
- Finally, modern electronics are expected to operate in increasingly compact spaces. The need for smaller, lighter devices with improved performance means that traditional cooling methods, such as large heat sinks or fans, are often impractical. Tubed cold plates address these challenges by providing a highly efficient and compact solution that can effectively dissipate heat in even the most space-constrained environments.
How Do Tubed Cold Plates Work?
Now that we have an understanding of what tubed cold plates are and why they are needed, let’s dive into how they work to manage heat in electronic systems.
- Heat Absorption: The process begins when the tubed cold plate is attached to a heat-generating electronic component, such as a CPU, GPU, or power supply. The plate is typically in direct contact with the component, allowing it to absorb heat as the component operates.
- Heat Transfer Through the Plate: Once the plate absorbs heat from the component, the heat spreads throughout the conductive material of the plate. The plate’s high thermal conductivity ensures that the heat is evenly distributed across the surface, preventing hot spots that could lead to thermal stress.
- Coolant Circulation: Inside the plate, there are tubes through which a coolant circulates. The coolant absorbs the heat from the plate and moves through the system to be dissipated elsewhere. As the coolant moves through the tubes, it picks up the absorbed heat and carries it away from the component.
- Heat Dissipation: The heated coolant exits the tubed cold plate and typically flows into a radiator or heat exchanger, where it releases the absorbed heat into the surrounding environment. In some systems, fans or additional cooling mechanisms are used to accelerate the heat dissipation process.
- Continuous Cycle: The coolant continues to circulate through the tubes, constantly absorbing and dissipating heat, ensuring that the electronic component remains at a stable and safe temperature. This cycle repeats continuously as long as the system is running.
The Benefits of Tubed Cold Plates
The use of tubed cold plates in thermal management offers numerous advantages that make them an attractive solution for a wide range of industries. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Superior Thermal Efficiency
One of the main reasons why tubed cold plates are revolutionizing thermal management is their superior efficiency in heat transfer. By using a network of tubes to circulate coolant, these systems can dissipate heat much more effectively than traditional air cooling solutions. The combination of high thermal conductivity materials and a large surface area for heat exchange ensures that tubed cold plates can maintain low temperatures, even under heavy load.
2. Compact and Space-Saving
As electronics continue to shrink in size, the need for space-efficient cooling solutions becomes increasingly important. Tubed cold plates are designed to be compact, fitting into small spaces without compromising cooling performance. Unlike bulky heat sinks or fans, tubed cold plates provide a high level of cooling in a slim and unobtrusive form, making them ideal for use in tight spaces such as small form-factor PCs, medical devices, or telecommunication equipment.
3. Improved Reliability and Performance
Maintaining optimal temperatures is key to ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic systems. By preventing components from overheating, tubed cold plates help avoid thermal throttling, where the CPU or GPU slows down to prevent damage from excessive heat. With the ability to maintain consistent and low temperatures, these coolers ensure that your system can run at full capacity, even during demanding tasks.
4. Low Maintenance
Unlike air cooling systems, which require regular cleaning and maintenance to prevent dust buildup, tubed cold plates are relatively low-maintenance. Once installed, they can operate effectively without the need for frequent intervention. This makes them a practical solution for systems that require continuous uptime, such as servers or industrial equipment.
5. Customization for Specific Applications
Tubed cold plates are highly customizable, allowing engineers to tailor them to the specific needs of the application. They can be designed with different tube configurations, coolant types, and materials to optimize heat transfer for particular electronic components or environments. This flexibility makes them suitable for a wide range of industries, including gaming, telecommunications, medical, automotive, and aerospace.

Applications of Tubed Cold Plates
The versatility of tubed cold plates makes them suitable for a broad array of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial systems. Some of the most common applications include:
- High-Performance Computing: In gaming PCs, servers, and workstations, tubed cold plates are used to cool CPUs, GPUs, and other high-performance components, ensuring stable and efficient operation during intense workloads.
- Telecommunications Equipment: Telecommunication devices, such as base stations and routers, generate substantial heat. Tubed cold plates provide an effective and compact solution for keeping these devices cool and ensuring uninterrupted service.
- Electric Vehicles: The electronics in electric vehicles (EVs), particularly in battery management systems and power electronics, require effective thermal management. Tubed cold plates are ideal for cooling these components, extending the life of the vehicle’s electronics.
- Medical Devices: Medical devices, especially those used in diagnostic imaging and patient monitoring, often rely on complex electronics that need to stay cool to operate properly. Tubed cold plates offer a reliable and efficient cooling solution in these environments.
Tubed cold plates have emerged as a revolutionary solution in the field of thermal management, offering superior cooling efficiency, compactness, and versatility. As electronic components continue to grow more powerful and compact, the need for advanced cooling solutions has never been more critical. Tubed cold plates provide the perfect solution to meet these challenges, ensuring that electronics operate reliably and efficiently under even the most demanding conditions.
At Tone Cooling Technology Co., Ltd., we are proud to offer state-of-the-art tubed cold plates that are designed to meet the unique thermal management needs of various industries. Whether you are working with high-performance computing systems, telecommunications equipment, or medical devices, our tubed cold plates provide the cooling efficiency and reliability.