A dual power supply is an important part of many electronic devices, especially circuits that require both positive and negative voltages to function properly. These power supplies are often used in devices such as amplifiers, sensors, and communication equipment. Understanding how a dual power supply works and its circuit diagram is important for anyone in the electronics field.
What is a dual power supply?
A dual power supply provides two different voltages: one positive and one negative. Both refer to a common ground. The main reason for using a dual power supply is that some circuits require both positive and negative voltages to function properly. For example, op-amps (operational amplifiers) often require dual power supplies to process signals properly.
In simple terms, a dual power supply provides two voltage sources, which are important for circuits that handle AC signals or differential signals. Without them, the circuit will not function properly.
Components Used in a Dual Power Supply
Several key components are used to build a dual power supply. Each part plays a specific role in providing the correct voltage:
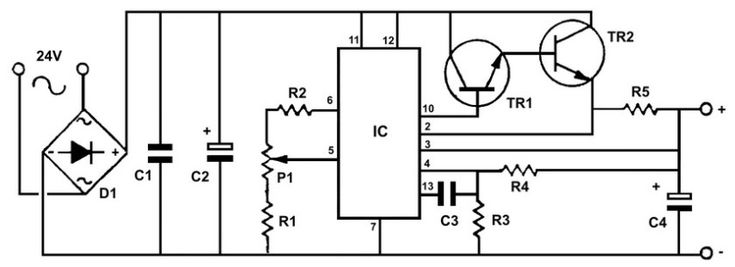
Transformer: The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the main power supply to a lower level. A center-tapped transformer is often used, which provides both positive and negative voltages, with the center tap acting as ground.
Rectifier: The rectifier converts the AC voltage to a DC voltage. A bridge rectifier is commonly used, which is made up of four diodes arranged in a way that converts AC to DC. Depending on how the transformer is connected, the output will have both positive and negative DC voltages.
Filter Capacitors: After the rectifier, the DC voltage still has some ripples. These ripples are smoothed out by the capacitors, which help create a stable DC voltage.
Voltage Regulators: Voltage regulators ensure that the voltage remains stable even if the input voltage or load changes. Common voltage regulators for dual power supplies include the 7812 for positive voltage and the 7912 for negative voltage.
Grounding: Proper grounding is key. The center tap of the transformer is connected to the ground, and both the positive and negative voltages refer to this common ground. A stable ground is important for accurate operation.
Circuit Construction
Here is a simple breakdown of how to build a dual power supply:
Step 1: Input AC Voltage First, the power supply receives AC voltage from the wall socket. This AC voltage is usually 120V or 240V, depending on the area. This voltage is sent to a transformer to be stepped down to the desired level.
Step 2: Transformer and center tap The transformer steps down the AC voltage to a lower value. A center-tapped transformer is used, where the center tap acts as ground. For example, to get ±12V, the transformer will provide 24V AC.
Step 3: Rectification with a bridge rectifier The AC voltage from the transformer is sent to a bridge rectifier. The rectifier changes the AC voltage into a pulsating DC voltage. The output will have both positive and negative rails since the center tap is grounded.
Step 4: Filtering After rectification, the DC voltage is still not completely smooth. Large capacitors are used to filter out the ripples and stabilize the DC voltage.
Step 5: Voltage Regulation After filtering, voltage regulators, such as the 7812 (for positive voltage) and 7912 (for negative voltage), are used to keep the voltage stable. These regulators ensure that the output voltage remains at a fixed level (e.g., ±12V), even if the input or load fluctuates.
Step 6: Output DC Voltage Finally, the dual power supply is ready to provide the positive and negative DC voltages needed to power the circuit.
How Dual Power Supplies Work
Here is how a dual power supply works in simple terms. First, the AC voltage from the wall socket is stepped down by a transformer. Then, a rectifier changes this AC voltage to DC. Capacitors smooth out any ripples in the DC voltage, and the voltage regulator ensures that the output voltage is stable.
The most important thing to remember is that a dual power supply provides two separate voltages: one positive and one negative, both referenced to the same ground. This allows circuits to function properly when they require both positive and negative voltages.
Uses of Dual Power Supplies
Dual power supplies are used in many types of electronic systems, such as:
Operational amplifiers (op-amps): Op-amps typically require dual power supplies to function properly, as they require both positive and negative voltage rails.
Analog circuits: Many analog circuits, such as audio amplifiers, use dual power supplies to keep the signal clean and stable.
Audio Systems: Audio systems, such as mixers and amplifiers, often use dual power supplies to ensure high-quality sound.
Test Equipment: Oscilloscopes, signal generators, and other test equipment rely on dual power supplies for accurate signal analysis.
Communication Systems: Communication devices such as transceivers require dual power supplies to handle positive and negative voltage levels for effective signal transmission.
Conclusion
A dual power supply is an essential component for many electronic circuits, providing both the positive and negative voltages required for the proper functioning of complex systems. The construction includes simple yet important components such as transformers, rectifiers, capacitors, and voltage regulators, which work together to provide stable and stable power.
At Magnificette, we offer a variety of solutions for your power supply needs, ensuring reliable and efficient operation for your projects.