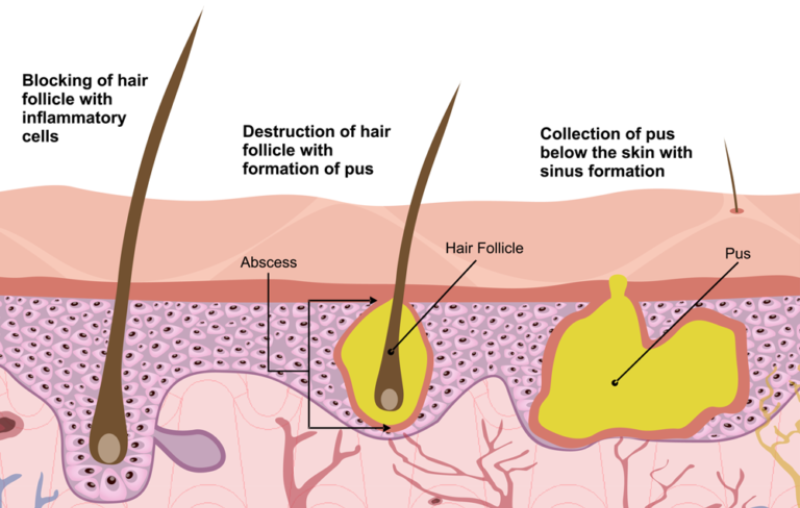
The rare Chronic Skin Condition known commonly as hidradenitis suppurativa, more accurately called acne inversa, manifests with painful, inflamed nodules usually hidden from view. Lumps frequently form in axillary areas, the groin, the genital region, underneath breasts, the intergluteal area, and in the perianal regions.
What makes HS really bad is that it just persists over time, even deteriorating in a great percentage of cases, and has such a hard-to-mimic pattern and difficulty to manage for a patient.
Hidradenitis suppurativa Symptoms
The disease is defined by characteristic clinical manifestations. The main symptoms are painful swollen nodes, from which pus and blood are released, and the formation of fistulas. Such manifestations of the disease as severe pain, limited joint mobility, and fistulas with discharge that has an unpleasant odor lead to a decrease in self-esteem and performance, the development of depression, and social isolation of patients.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treatment often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical intervention to manage these symptoms effectively.
Typical places where nodes and fistulas appear are:
- Axillary region
- Under the mammary glands
- Groin area
- Inner thighs
- Buttocks
- In the anal area
Subsequently, scars form in the area of the nodes.
Diagnosis
Currently, there is no instrumental or laboratory test capable of revealing the presence of hidradenitis suppurativa hs; therefore, to diagnose the latter, doctors can only rely on the information coming from the objective examination and the anamnesis, in relation to the symptoms, and proceed by exclusion (the so-called differential diagnosis ).
Physical examination and medical history
In the context of Hidradenitis Suppurativa, the physical examination and anamnesis consist essentially of a critical evaluation of the symptoms; in addition to a careful observation of the signs present on the patient’s body, they include questions relating to:
- The symptoms (e.g. when did the first symptoms appear? Did the symptoms arise after a particular event? Etc.);
- General health status ( these questions are aimed at identifying those conditions usually related to the presence of hidradenitis suppurative, such as metabolic syndrome, diabetes, etc.);
- Family history ( these are questions aimed at discovering whether there are other subjects in the patient’s family with the same symptoms; the possible genetic-hereditary nature of hidradenitis explains such research).
Differential diagnosis
Within the diagnostic process that leads to the identification of hidradenitis suppurativa, the differential diagnosis consists mainly of blood tests, performed to exclude that the current symptoms may depend on some infectious disease.
Therapy
Although there is currently no cure for hidradenitis suppurativa, patients can now manage their symptoms, slow the disease’s progression, and prevent many complications thanks to improvements in symptomatic treatments. Some people even notice unexpected improvements. It is important to understand that while there are various symptomatic Hidradenitis Suppurativa treatment options, not all are suitable for every patient, and the best course of action is to begin treatment as soon as possible to significantly improve the chances of better results.
Symptomatic pharmacological treatments
Hidradenitis suppurativa symptom management involves various drug classes:
- Antibiotics: Oral or topical treatments like tetracyclines and rifampicin reduce inflammation.
- Retinoids: Help certain patients. Examples: isotretinoin.
- Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation; injectables target specific areas. Examples: prednisolone.
- Immunosuppressants: Useful for immune-related cases. Examples: adalimumab.
- Hormonal Therapy: For women with cyclical symptoms. Not for pregnancy.
- Analgesics: Pain management options like fentanyl.
Symptomatic surgical treatments
Hidradenitis suppurativa surgery is an option reserved for the most severe cases. This includes instances where other treatments don’t work, the disease causes repeated nodules, or there’s significant skin damage from ongoing flare-ups. Surgery is also considered when painful, infected wounds become a major concern. Several surgical approaches exist to manage advanced hidradenitis suppurativa, including:
- The operation of incision and surgical drainage of the nodules;
- Laser ablation of nodules and subcutaneous interconnections (tunnels);
- Nodule curettage, followed by the de-roofing of the connecting tunnels;
- The so-called punch debridement for the elimination of individual nodules;
- Removal of the affected tissues by electrosurgery ;
- Total surgical removal of the affected tissues;
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle and a few “home remedies” can help patients with hidradenitis suppurativa in addition to the therapeutic approaches already mentioned.
Regarding at-home treatments, we advise using antiseptic soaps to clean wounds, applying warm, moist compresses to the afflicted areas to relieve pain, dressing comfortably and loosely because tight clothing exacerbates symptoms, and refraining from using deodorant of any kind.
However, when it comes to leading a healthy lifestyle, actions like regularly engaging in physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing body weight (if there is an obesity issue) are noteworthy.
Final Words
Although hidradenitis suppurativa is a difficult condition, patients can greatly improve their quality of life and reduce their symptoms with the correct combination of treatments. To stop progression, early diagnosis, good symptom management, and lifestyle changes are essential. The best treatment plan can be customized to meet each patient’s needs with the assistance of medical professionals.