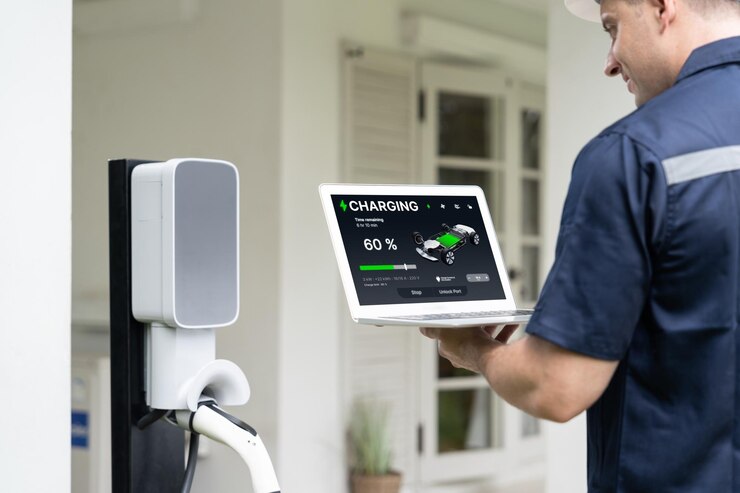
The increasing popularity of EVs makes home charging solutions not just a want but a must be. Having a charger at home is very convenient and, above all, as sure a thing as driving your vehicle when you feel like doing so. All that is needed now is to know the several EV Charger Installation Requirements before commencing with the installation to ensure that it is safe and functional. In this guide, we’ll be going over all the specifics you should know, from electrical capacity to location considerations, permitting processes, and much more.
1) Understanding the Types of EV Chargers:
You’ll need to know which of the following types of EV chargers you’ll be having installed. There are three types:
i) Level 1 Chargers:
These run on 120-volt power and are the slowest of the three. They require no special installation but are only suitable for very occasional use-they add a few miles of range per hour of charging.
ii) Level 2 Chargers:
A Level 2 charger is the most common home installation. It is charged from a 240V outlet, similar to a dryer. Level 2 chargers charge at much faster rates than Level 1.
iii) Level 3 Chargers (DC Fast Chargers):
DC Fast Chargers are mostly seen at public or commercial locations. Installation costs for a DC Fast Charger are expensive. Like the Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, though it can charge the battery of an electric vehicle at any point in time in a matter of minutes for its long life cycle, DC Fast Chargers are not so ideal for home usage.
Most homeowners install a Level 2 charger at home because it offers the right balance of speed and affordability. Now that you know what type of chargers are available, let’s consider the requirements needed to install one.
2) Electrical Capacity and Upgrades:
Actually, one of the more important requirements of installing an EV charger at your house is that you ensure your house’s electrical system is ready to handle the extra load from a Level 2 charger. A Level 2 charger requires a circuit with 240 volts, but such a circuit does not exist in most home outlets. It can even necessitate an upgrade of your electrical panel to install one of these chargers.
The electrical capacity will be reviewed and the foreman contacted in order to find out if the present capacity can carry added load. In such houses where electricity systems are old, the panel may require an upgrade, which involves installing a new circuit breaker and wiring for carrying extra load.
The dedicated 30-60 amp circuit usually recommended for a Level 2 EV charger depends on the specific model. Upgrading your electrical panel cost may range between $500 to $2,500, depending on your home’s needs and complexity of the installation.
3) Location Considerations for Installation:
Location of EV charger would be a critical part of convenience and safety. The distance to where you would be parking your vehicle is something a charger must be located close enough to but not too close so as to cause obstruction or possible hazards.
Some of the selection criteria include:
i) Neatness of the Cable Approach:
The charging cable should be able to reach your car’s charging port, not too taut. In general, the length of the charging cable spreads within 12 up to 25 feet.
ii) Weather Protection:
Often, when the installations are outdoors, the equipment has to be weather-resistant. One must look for a place installing that does not expose it to direct exposure to the elements or is sheltered under a carport, garage, or something similar.
iii) Accessibility and Convenience:
Select a place where you can go to the charging station each day without hassle. It should also be closer to the parking place of your vehicle and the charge cable.
iv) Distance from the Electrical Panel:
Installation far away from the electrical panel causes additional wiring cost, which you do not want. Try to make the installation location nearer to the electrical panel so that you will not be forced to increase the costs.
4) Permit and Compliance with Local Building Codes:
It is a prerequisite to check with your local government before getting an EV charger for your house as you may be required to obtain a permit. In most jurisdictions, such installations require an electrical installation permit. Your licensed electrician will take care of the permit application most of the time, but is essential that you be in compliance with all local building codes and regulations.
Some typical EV Charger Installation Requirements that include permits and codes are:
i) Electrical Work Permits:
Often, a Level 2 charger is required by jurisdictions to be installed under an electrical permit. Your electrician will submit this permit on your behalf and schedule an inspection to be sure the work complies with the applicable building codes.
ii) Compliance with National and Local Codes:
Electrical installation should be in accordance with National Electric Code (NEC) and prevailing changes at the local levels. For example, NEC may require a GFCI to prevent the electrical shock possibility.
iii) Inspection:
After installation, there might be a need for an inspection to ensure that the installation meets the local building codes and is safe. An inspector will look at the safety of the electrical panel, wiring, and grounding.
5) Cost Considerations in Installing EV Charger:
The cost for the EV Charger Installation varies based on factors like the type of charger, installation location, and necessary electrical upgrade. Here’s a general breakdown of what to expect:
i) EV Charger Unit:
A level 2 charger unit typically costs between $400 and $1,200, depending on the brand and features, like Wi-Fi connectivity and smart charging.
ii) Upgrade Electrical Panel:
In case that an upgrade of your electrical system is in order, expect to spend a range from $500 to $2,500 including the cost of a new circuit breaker, wiring, and panel upgrade.
iii) Labor:
The rates of a licensed electrician for labor may run in a range between $50 and $150 per hour, depending on location and complexity. Installation of the unit may take about 4 to 8 hours, inclusive of setting up, wiring, and final inspection.
iv) Permits and Fees:
Depending on your location, there may be a fee to pay. Of course, this will be upwards of $50 and possibly as much as $500.
In all, the installation of an EV charger will cost between $1,000 and $3,000 more, depending on the scope of the work and whether or not electrical systems need to be upgraded.
6) Select a Professional EV Charger Installer:
While some homeowners might consider DIY installation, hiring a professional electrician is always the best solution for EV Charger Installation. A licensed, experienced installer will ensure that your charger is installed safely. At the same time, a professional will provide you with all the services for installation, fulfilling local codes. Other essential tasks that a professional will have to manage include getting the necessary permits, inspections, and required upgrades on your electrical system.
Other things you should know before hiring an installer include:
i) Experience and Licensing:
Ensure you pick an installer who has experience in installing EV chargers and proper licensing.
ii) References and Reviews:
Determine customer reviews and ask for references to ensure that the installer has a proven history of successful installations.
iii) Warranty:
The work should be warrantied by the installer, normally covering labor and materials for a period.
The Final Words:
Putting an EV charger in the house is one step closer to embracing sustainable driving; however, a person needs to know about the Ev Charger Installation Requirements before carrying on with the process. Right from electrical capacity and the need for the panel upgrade to positioning and acquiring permits, there are several factors to be considered for safe and efficient installation. By passing through a professional installer and meeting all requirements, you will surely love your home charging and contribute to a greener future.