Refined soybean oil is one of the most widely consumed vegetable oils in the world, used extensively in food processing, cooking, biodiesel production, and various industrial applications. The refined soybean oil price Forecast is influenced by a wide range of factors, including supply-demand dynamics, weather conditions, geopolitical developments, and global commodity markets. Understanding the factors driving refined soybean oil prices is critical for businesses in the food, agriculture, and energy sectors. In this article, we explore the key determinants of soybean oil prices, historical trends, and future price projections.
With the rising global population, increased demand for biofuels, and changing dietary patterns, the demand for edible oils, including soybean oil, has increased significantly. At the same time, environmental factors, trade policies, and market fluctuations contribute to the volatility in prices, making it essential for businesses to stay informed about price trends and projections.
Factors Influencing Refined Soybean Oil Price Trends
Several factors affect the price of refined soybean oil, ranging from raw material availability and global demand to production costs, weather conditions, and trade policies. These factors interact in complex ways, creating fluctuations in the price of soybean oil in global markets.
1. Supply and Demand Dynamics
Supply-demand balance is a fundamental driver of soybean oil prices. The production of soybeans, the raw material for soybean oil, and the global demand for edible oils are critical factors that determine the price trend.
- Soybean Production Levels: Soybean oil is extracted from soybeans, and the global supply of soybeans directly affects the availability and price of soybean oil. Major producers such as the United States, Brazil, and Argentina dominate the global soybean market. Any disruption in production due to adverse weather conditions, such as droughts or floods, can reduce supply and increase prices.
- Rising Demand for Edible Oils: The growing demand for edible oils in food processing, particularly in emerging markets such as India, China, and Southeast Asia, has led to increased consumption of refined soybean oil. The rise of processed foods, changing dietary preferences, and urbanization are key factors driving this demand.
- Biofuel Industry Demand: The growing use of soybean oil in the production of biodiesel also influences its price. As countries adopt renewable energy sources to reduce carbon emissions, the demand for biofuels, including biodiesel made from soybean oil, has surged, contributing to upward pressure on prices.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/refined-soybean-oil-price-trends/pricerequest
2. Weather Conditions and Climate Change
Weather conditions and climate change significantly impact the production of soybeans, which in turn affects the price of soybean oil.
- Adverse Weather: Droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures in major soybean-producing regions, such as the U.S. Midwest, Brazil, and Argentina, can negatively impact crop yields. Poor harvests due to adverse weather can lead to reduced soybean supply, pushing up the price of soybean oil.
- Climate Change: The long-term effects of climate change, such as unpredictable weather patterns and shifting agricultural zones, have the potential to disrupt soybean production. Climate-related factors will continue to play a critical role in shaping the supply of soybean oil, contributing to price volatility.
3. Trade Policies and Geopolitical Factors
Trade policies and geopolitical events have a significant impact on global soybean oil prices. Tariffs, trade agreements, and export restrictions can affect the flow of soybeans and soybean oil between countries.
- Tariffs and Trade Wars: Trade tensions between major agricultural exporters and importers can disrupt the global soybean oil supply chain. For example, trade disputes between the U.S. and China have historically influenced soybean prices, which in turn affect the price of soybean oil.
- Export Restrictions: Some countries may impose export restrictions on soybeans or soybean oil to ensure domestic food security or stabilize prices. These restrictions can reduce global supply and lead to price increases in international markets.
4. Currency Exchange Rates
Currency exchange rates play a key role in determining the cost of soybean oil, especially for countries that import large quantities of the commodity.
- U.S. Dollar Strength: Since soybeans and soybean oil are primarily traded in U.S. dollars, fluctuations in the value of the U.S. dollar relative to other currencies can impact the price of soybean oil. A stronger U.S. dollar typically makes soybean oil more expensive for importers, leading to reduced demand and downward pressure on prices. Conversely, a weaker U.S. dollar can make soybean oil more affordable for importers, potentially boosting demand and prices.
5. Production Costs
The cost of producing refined soybean oil, including raw materials, energy, and labor, influences the overall price of the product.
- Processing Costs: The process of extracting oil from soybeans and refining it into consumable form incurs various costs, including labor, equipment maintenance, and energy consumption. Fluctuations in these costs can affect the price of refined soybean oil.
- Input Costs: The price of inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides, and fuel can affect the overall cost of soybean production. Rising input costs for soybean farmers can lead to higher raw material costs, which are ultimately passed on to consumers in the form of higher refined soybean oil prices.
6. Competing Oils and Substitutes
Soybean oil competes with other edible oils, such as palm oil, sunflower oil, and canola oil, in the global market. Changes in the prices of these substitutes can influence the price of soybean oil.
- Palm Oil Prices: Palm oil is a major competitor to soybean oil and is often used as a substitute in food production and cooking. When palm oil prices rise, demand for soybean oil may increase, driving up its price. Conversely, when palm oil prices fall, the demand for soybean oil may decrease, putting downward pressure on prices.
- Other Vegetable Oils: The prices of other vegetable oils, such as sunflower oil and canola oil, also affect the demand and price of soybean oil. For example, a poor sunflower harvest may lead to increased demand for soybean oil, raising prices.
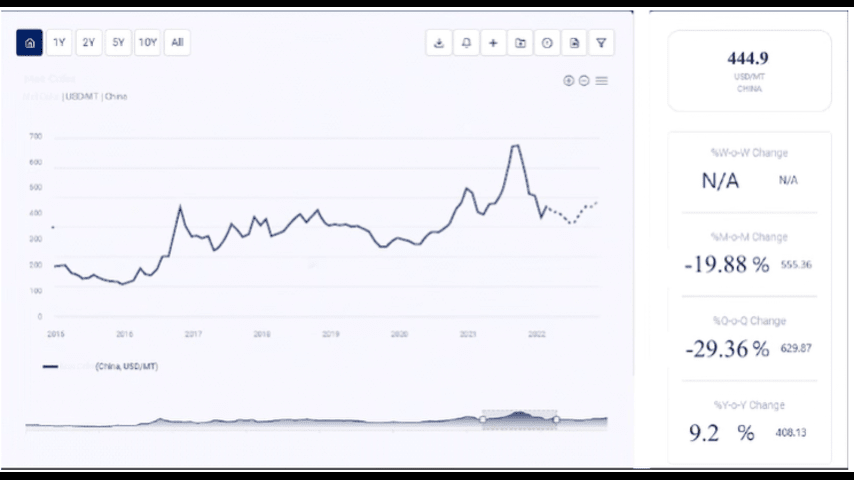
Historical Price Trends for Refined Soybean Oil
Pre-2020 Price Trends
Before 2020, the price of refined soybean oil was relatively stable, with moderate fluctuations driven by global soybean production levels, trade policies, and market demand for edible oils.
- Stable Supply and Demand: During this period, the global supply of soybeans was generally stable, with major producers such as the United States, Brazil, and Argentina consistently meeting global demand. Prices remained within a predictable range, influenced primarily by seasonal production cycles and agricultural yields.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic (2020-2021)
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on the global soybean oil market, leading to significant price volatility and disruptions in supply chains.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Lockdowns, labor shortages, and logistical challenges caused disruptions in the global supply chain, leading to delays in soybean harvesting, processing, and transportation. These disruptions contributed to a temporary spike in refined soybean oil prices.
- Increased Demand for Edible Oils: The pandemic led to a surge in demand for edible oils as consumers stockpiled food products. Additionally, more people cooking at home increased the consumption of cooking oils, including soybean oil, further driving up prices.
Post-Pandemic Recovery (2022-Present)
In 2022 and beyond, refined soybean oil prices began to stabilize as supply chains recovered from the disruptions caused by the pandemic. However, prices remained elevated due to several persistent factors.
- Rising Input Costs: The cost of agricultural inputs, such as fertilizers and fuel, increased due to global inflationary pressures, adding to the production cost of soybeans and soybean oil. This led to higher prices for refined soybean oil.
- Continued Demand for Biodiesel: The ongoing demand for biodiesel, driven by renewable energy policies, has continued to support high soybean oil prices. As governments around the world push for cleaner energy sources, soybean oil has emerged as a key feedstock for biodiesel production.
Future Price Outlook for Refined Soybean Oil
Several factors will shape the future trend of refined soybean oil prices, including production levels, demand for biofuels, climate change, and global trade dynamics.
- Climate Impact on Production: Climate change and its impact on weather patterns will remain a critical factor in determining soybean yields. Adverse weather events such as droughts or floods in major soybean-producing regions may result in reduced output, putting upward pressure on prices.
- Biofuel Demand: The growing emphasis on renewable energy and the transition to cleaner fuels will likely continue to support demand for biodiesel made from soybean oil. This increased demand for soybean oil in the energy sector may contribute to sustained high prices.
- Global Trade Relations: Ongoing trade negotiations and policies between major soybean producers and importers will influence global supply and demand. Any disruptions in trade, such as tariffs or export restrictions, may lead to price fluctuations in the refined soybean oil market.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: [email protected]
Toll-Free Numbers:
- USA & Canada: +1 307 363 1045
- UK: +44 7537171117
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA