Production operators are the backbone of manufacturing and industrial sectors, responsible for overseeing the smooth running of machinery and production lines. Their roles include operating equipment, ensuring production standards are met, troubleshooting issues, and maintaining quality control. As industries expand and technological advancements reshape production processes, the demand for skilled production operators continues to grow. Understanding the
production operator wages trend is crucial for businesses to remain competitive, optimize labor costs, and attract top talent in an increasingly competitive labor market.
This article will provide a detailed analysis of the factors influencing production operator wages, historical wage trends, and future wage projections. It also explores regional differences in pay rates and the impact of economic conditions on the compensation for production operators. This analysis will help companies better manage their labor strategies, recruitment efforts, and budget planning.
1. Overview of Production Operator Roles and Responsibilities
What is a Production Operator?
A
production operator is responsible for running, maintaining, and troubleshooting machines or equipment involved in manufacturing. They are critical to ensuring that production processes run efficiently and meet established quality standards. Depending on the industry, production operators may work with assembly lines, food processing plants, chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, automotive manufacturing, or electronic component production.
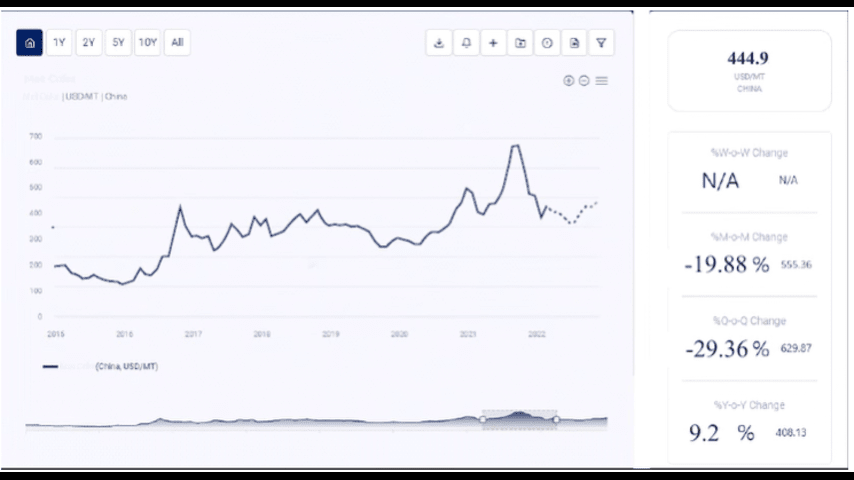
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/production-operator-price-trends/pricerequest
Key Responsibilities of Production Operators
- Machine Operation: Operating machinery and equipment used in the production process, ensuring smooth and continuous operation.
- Quality Control: Monitoring the production output to ensure that it meets specified quality standards and identifying any defects or issues that may arise.
- Troubleshooting: Detecting and solving problems with machinery, equipment, or production processes.
- Safety Compliance: Following safety protocols and procedures to ensure a safe working environment for themselves and others.
- Record Keeping: Keeping detailed records of production activities, including output, quality control checks, and equipment maintenance logs.
2. Factors Influencing Production Operator Wage Trends
Several factors drive the wage trends of production operators, including the level of skill required, geographic location, demand for skilled labor, technological advancements, and macroeconomic conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for both employers and job seekers in determining competitive wage rates and compensation packages.
a. Skill Level and Experience
Wages for production operators vary based on their skill level, qualifications, and years of experience. Operators with specialized knowledge, such as those who work with complex machinery, robotics, or programmable logic controllers (PLCs), typically command higher wages compared to those in more routine roles.
- Skill Level: Operators with advanced technical skills or certifications (e.g., CNC machine operation, mechatronics, or robotic automation) often earn higher wages due to their expertise in handling sophisticated equipment and technologies.
- Experience: More experienced operators who have worked across different production environments or have specialized knowledge of a particular industry tend to earn more compared to entry-level operators. Experience in troubleshooting and maintaining complex machinery is highly valued.
b. Industry-Specific Demand
Wage trends for production operators are also heavily influenced by industry-specific demand. Certain industries, such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and high-tech manufacturing, typically offer higher wages due to the specialized nature of the work and the need for highly skilled operators.
- Manufacturing Industry: In industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where precision and adherence to stringent safety standards are critical, production operators with advanced skills are in high demand. Consequently, these industries often offer competitive wages to attract top talent.
- Pharmaceutical and Food Processing: In sectors like pharmaceuticals and food processing, where adherence to hygiene and safety regulations is critical, production operators are required to follow strict protocols, resulting in higher compensation for those with specialized training.
c. Geographic Location and Regional Differences
Wages for production operators can vary significantly based on geographic location. Factors such as local cost of living, demand for skilled labor, and regional economic conditions play a key role in determining compensation.
- Urban vs. Rural Areas: Operators working in urban areas or regions with a higher cost of living tend to earn higher wages than those in rural areas. In densely populated areas, industries often face greater competition for skilled workers, driving up wages.
- Regional Industrial Hubs: Production operators working in regions with a high concentration of manufacturing facilities or industrial hubs (e.g., the Midwest in the U.S., or Bavaria in Germany) typically enjoy higher wages due to increased demand for labor in these areas.
d. Impact of Technological Advancements
Advances in automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence (AI) have reshaped the role of production operators. While these technologies can reduce the need for manual labor, they also increase the demand for highly skilled operators who can manage, troubleshoot, and maintain automated systems.
- Automation and Robotics: As manufacturing processes become more automated, there is a growing demand for production operators with skills in operating and maintaining advanced machinery and robotic systems. These specialized roles typically come with higher wages due to the technical expertise required.
- Digital Skills: Operators who possess digital skills, such as familiarity with machine learning systems, smart factory technology, and data analytics, are increasingly sought after. This shift toward more technologically advanced operations has contributed to wage growth for skilled production operators.
e. Economic Conditions and Labor Market Trends
Broader economic conditions and labor market trends play a significant role in determining production operator wages. Factors such as labor shortages, inflation, unemployment rates, and the overall health of the economy impact wage levels in this sector.
- Labor Shortages: In periods of labor shortages, companies may raise wages to attract and retain qualified production operators. The manufacturing sector has experienced labor shortages in recent years, partly due to an aging workforce and a lack of younger workers entering the industry.
- Inflation and Cost of Living: Rising inflation and increases in the cost of living can also lead to wage growth, as employers adjust compensation to ensure that workers can afford basic necessities and maintain their standard of living.
f. Union Influence
In certain industries or regions, labor unions play a critical role in influencing wage trends for production operators. Unions often negotiate wage increases, benefits, and working conditions on behalf of workers, which can lead to higher overall compensation packages.
- Unionized Workplaces: Production operators working in unionized environments may enjoy higher wages compared to those in non-unionized workplaces. Union contracts typically include regular wage increases, improved benefits, and job security provisions, which can contribute to higher compensation.
3. Historical Wage Trends for Production Operators
a. Pre-2020 Stability
Prior to 2020, wages for production operators experienced relatively steady growth, driven by the increasing demand for skilled labor in manufacturing and industrial sectors. The wage growth in this period was largely influenced by technological advancements, the rise of automation, and moderate inflation.
b. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic (2020-2021)
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound effect on the labor market, including wages for production operators. During the initial stages of the pandemic, many manufacturing facilities faced shutdowns or reductions in capacity, leading to layoffs and furloughs. However, as the economy recovered, production operators became critical to resuming operations and meeting increased demand for essential goods.
- Initial Decline: In the early months of the pandemic, wages for production operators were affected by reduced manufacturing activity, particularly in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
- Post-Pandemic Recovery: As manufacturing facilities adapted to the new normal, demand for production operators surged. Essential sectors such as food production, healthcare supplies, and e-commerce logistics drove wage growth as manufacturers ramped up production. The increased focus on health and safety protocols also led to higher demand for skilled workers.
c. Post-Pandemic Recovery (2022-Present)
As the global economy rebounded from the pandemic, wages for production operators saw significant upward pressure. Labor shortages, particularly in manufacturing, logistics, and supply chain sectors, led to increased competition for skilled labor.
- Rising Wages: Employers across various industries, including automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods, raised wages to attract and retain skilled production operators. The ongoing shift toward automation and digitalization further increased the demand for tech-savvy operators.
- Inflationary Pressures: Inflation has also played a role in wage increases, as companies adjusted wages to keep pace with rising costs of living and ensure competitive compensation packages.
4. Future Wage Projections for Production Operators
Several factors will continue to influence the future wage trends for production operators. The ongoing technological evolution, changes in labor market conditions, and the impact of globalization will shape wage dynamics in this sector.
- Continued Demand for Skilled Labor: The demand for highly skilled production operators is expected to remain strong, particularly in industries that rely heavily on advanced technology and automation. Operators with specialized skills in robotics, CNC machining, and digital factory operations will likely command higher wages.
- Inflation and Economic Recovery: As inflationary pressures persist, companies may need to continue raising wages to attract and retain workers, especially in regions with higher living costs. The recovery of the global economy will also play a role in determining wage growth in the coming years.
- Technological Adaptation: With the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, production operators will need to continually upgrade their skills to remain competitive. This shift may lead to higher wages for those with expertise in operating and maintaining advanced machinery and software systems.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: [email protected]
Toll-Free Numbers:
-
- USA & Canada: +1 307 363 1045
-
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA