This improves the company’s asset turnover ratio in the short term as revenue (the numerator) increases as the company’s assets (the denominator) decrease. The asset turnover ratio calculation can be modified to omit these uncommon revenue occurrences. It is the gross sales from a specific period less returns, allowances, or discounts taken by customers.
Low asset turnover ratio interpretation
However, it’s important to consider asset turnover in conjunction with other financial metrics and qualitative factors to get a more complete picture of the company’s financial health. Your asset turnover ratio is an equation to help you figure out how you’re using your assets to generate sales. In much simpler terms, by finding your asset turnover, you can self billing of tax invoices figure out how many dollars of sales you’re generating for every dollar in the value of assets you have. This accounting principle is a peek into the efficiency of your business—whether or not you’re using the assets you have, both fixed and current, to generate sales. If the asset turnover ratio of a company is less than 1, it is said to have a low ratio.
DuPont Analysis
Therefore, a higher value of this ratio is usually interpreted as a company using its assets well enough to generate its net sales or revenue. In this article, we will discuss the asset turnover ratio interpretation and how to interpret it with examples. A company may have record sales and efficiently use fixed assets but have high levels of variable, administrative, or other expenses. Companies with higher fixed asset turnover ratios earn more money for every dollar they’ve invested in fixed assets. Manufacturing companies often favor the FAT ratio over the asset turnover ratio to determine how well capital investments perform. Companies with fewer fixed assets such as retailers may be less interested in the FAT compared to how other assets such as inventory are utilized.

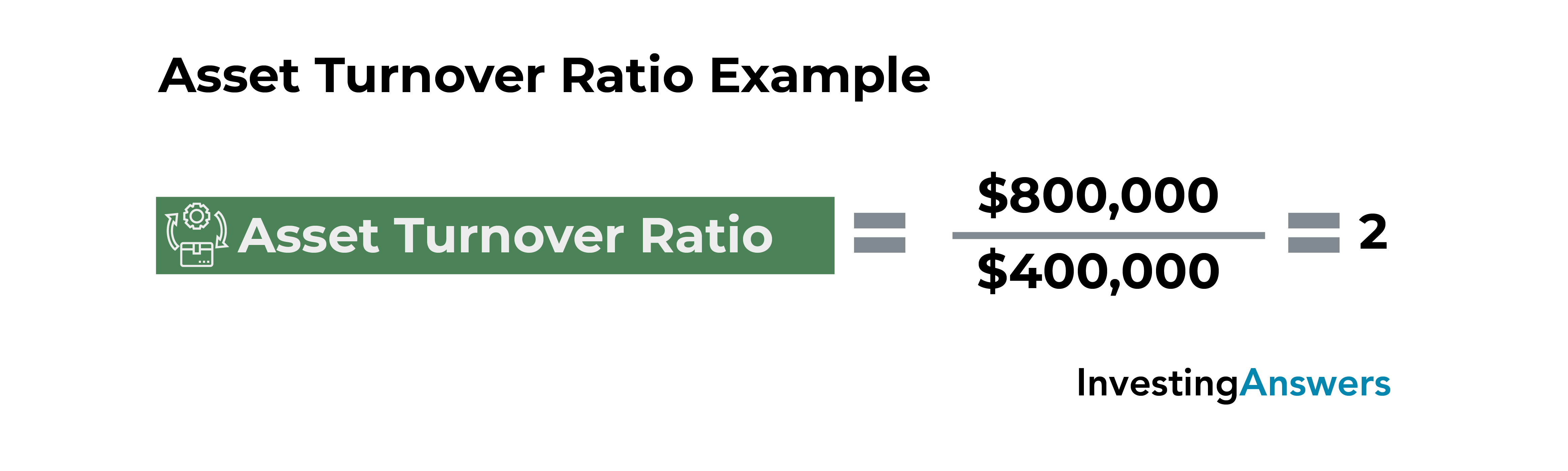
Interpreting results from the total asset turnover calculator
Transitioning from what this ratio represents, we delve deeper into its application, interpretation, and the caution required when comparing across diverse industry landscapes. Thomas J Catalano is a CFP and Registered Investment Adviser with the state of South Carolina, where he launched his own financial advisory firm in 2018. Thomas’ experience gives him expertise in a variety of areas including investments, retirement, insurance, and financial planning. For Year 1, we’ll divide Year 1 sales ($300m) by the average between the Year 0 and Year 1 PP&E balances ($85m and $90m), which comes out to a ratio of 3.4x. For the final step in listing out our assumptions, the company has a PP&E balance of $85m in Year 0, which is expected to increase by $5m each period and reach $110m by the end of the forecast period.
Managing Uncollected Protection Deposits in Finance
This is not considered good for the company because it indicates that the company’s total assets cannot produce enough revenue at the end of the accounting period (usually a year). However, this interpretation and conclusion still depend on the average asset turnover ratio of the industry to which the company belongs. Other business sectors like real estate normally take long periods of time to convert inventory into revenue. Hence, the industry-wide asset turnover ratio is usually low even though real estate transactions may result in high-profit margins.
- When comparing the asset turnover ratio between companies, ensure the net sales calculations are being pulled from the same period.
- A high asset turnover ratio indicates a company that is exceptionally effective at extracting a high level of revenue from a relatively low number of assets.
- Depreciation is the allocation of the cost of a fixed asset, which is expensed each year throughout the asset’s useful life.
- While asset turnover provides a lens into operational efficiency, ROA offers a broader view of overall profitability.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
In simple terms, the company is creating more sales per dollar of assets, indicating efficient asset management. In the realm of financial analysis, the Asset Turnover Ratio plays a critical role. It provides significant insights into how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales. Sally’s Tech Company is a tech start up company that manufactures a new tablet computer. Sally is currently looking for new investors and has a meeting with an angel investor. The investor wants to know how well Sally uses her assets to produce sales, so he asks for her financial statements.
When comparing the asset turnover ratio between companies, ensure the net sales calculations are being pulled from the same period. The asset turnover ratio formula can help you figure out a precise answer to this business finance question. As the asset turnover ratio varies across business sectors, some industries tend to have a higher ratio while some tend to have a lower ratio. Interpreting the asset turnover ratio requires a nuanced approach, as the figure alone does not paint a complete picture of a company’s performance.
Asset turnover ratios vary across different industry sectors, so only the ratios of companies that are in the same sector should be compared. For example, retail or service sector companies have relatively small asset bases combined with high sales volume. Meanwhile, firms in sectors like utilities or manufacturing tend to have large asset bases, which translates to lower asset turnover. Sometimes investors also want to see how companies use more specific assets like fixed assets and current assets. The fixed asset turnover ratio and the working capital ratio are turnover ratios similar to the asset turnover ratio that are often used to calculate the efficiency of these asset classes.
The Asset Turnover Ratio is a performance measure used to understand the efficiency of a company in using its assets to generate revenue. It measures how effectively a company is managing its assets to produce sales and is a key indicator of operational efficiency. A higher ratio suggests that the company is using its assets more effectively to generate revenue.
